Heating system installation
Cosiness and comfort at home depends on many factors. One of the main is home heating. Doing the installation of a heating system with your own hands is quite possible. But in order to avoid mistakes and get a high-quality result, you need to understand the basics of the installation process and determine the type and method of heating.
First of all, you need to calculate such parameters as the area and number of rooms, the amount of time during which you need to turn on the heating. And determine the choice of radiators, pipes and make a list of necessary tools and materials.
Necessary tools
First, consider a number of tools for work. Some of them are quite specific and will be needed just once, so look for, ask friends, so as not to waste money.
- Hammer, ruler, tape measure, pencil;
- Fum tape, paste for sealing threaded joints;
- Sandpaper, hedgehog;
- Level (can be laser - save time);
- Adjustable wrench and wrench (preferably small and large of each type);
- Screwdriver or set screwdrivers;
- Drill, in some cases hammer drill;
- Manual or electric pipe cutter;
- Bulgarian;
For plastic pipes:
- Apparatus for soldering plastic pipes with various nozzles;
For copper pipes:
- Blowtorch for brazing copper pipes;
- Solder for copper pipes, flux paste;
Types of Radiators
This is one of the most important points. It is through radiator the air and the room itself are heated. When choosing the type of heating element Be guided not only by appearance and aesthetics, but also by its main characteristics: power, working and maximum pressure and working temperature. This is especially important if you plan to connect it to a centralized heating system, where 4-10 atmospheres of normal operating pressure. And with the onset of the heating period, it increases by one and a half times (to check for leaks).
But if autonomous heating is planned, then these nuances disappear. You will have enough radiator working under pressure up to 6 atmospheres.
The most popular today are 4 types: aluminum, steel, bimetallic and cast iron radiators.
Aluminum radiators
 Aluminum radiators are considered very effective due to the large heat transfer of the material. After switching on, these radiators will quickly heat the room and cool off just as quickly if you turn off the heating. This is also due to the small volume of the device.
Aluminum radiators are considered very effective due to the large heat transfer of the material. After switching on, these radiators will quickly heat the room and cool off just as quickly if you turn off the heating. This is also due to the small volume of the device.
Very often, aluminum radiators are installed together with a regulating thermal head to automatically increase or decrease the supply of hot water.
Outside, aluminum radiators are very aesthetic. Rectangular plates, mostly white, coated with special heat-resistant enamel, which is resistant to high temperatures. This is another plus, since it will not be necessary every year paint again. Like cast iron radiators, in aluminum, you can increase power by changing the number of sections. They are not susceptible to condensation and humid air, so they can be safely used in the bathroom and in the kitchen.
If the advantages of this type of radiator are light weight, high working pressure and compactness, then of the minuses is the possibility of corrosion. Aluminum easily reacts with copper parts, and it also can not tolerate a large pH level (permissible 7.5). For this reason, it is better not to use them for a centralized heating system.
In connection with possible chemical reactions, aluminum radiators are mounted together with a Majewski faucet to divert the resulting gas.
Another minus when used in the central heating system is the operating temperature. For aluminum radiators it is 45-60 degrees, and in the central heating system it can reach 85 degrees.
Steel radiators
Modern steel radiators have a very attractive design. Like aluminum, they are coated with a special paint, mostly white, but can be painted in any shade according to the customer's request. The advantage of such radiators is their relatively low price and high heat transfer. Also, this type of radiator is one of the most hygienic.
There are two types of steel radiators - panel and tubular.
Panel
 This type has been used in the heating system for about 60 years. Working pressure is quite high and reaches 10 atmospheres.
This type has been used in the heating system for about 60 years. Working pressure is quite high and reaches 10 atmospheres.
The design of the radiator is made up of welded steel plates, which create the panel. Inside, between the panels are horizontal collectors and sometimes a convective lattice, so that the space warms up quickly enough. Several threaded connections in these radiators minimize leakage risk.
Of the minuses, a small radiator area can be distinguished, and susceptibility to corrosion processes under the influence of oxygen in the coolant, but this is not a problem with a closed heating system.
Tubular
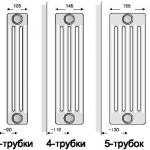 These radiators primarily differ from the panel type in a much larger heating area. You can adjust the power at the stage of purchase (order) by increasing / decreasing the height of the pipes, and their number. On the topic of color and coating, everything is the same as in panel.
These radiators primarily differ from the panel type in a much larger heating area. You can adjust the power at the stage of purchase (order) by increasing / decreasing the height of the pipes, and their number. On the topic of color and coating, everything is the same as in panel.
 Big plus of this type there is the possibility of creating a variety of radial or angular convector shapes.
Big plus of this type there is the possibility of creating a variety of radial or angular convector shapes.
 The design itself is represented mainly by vertical pipes forming sections with a width of up to 45 cm which are connected by welding collectors. The working pressure is also 10 atmospheres, and the temperature is 120 degrees.
The design itself is represented mainly by vertical pipes forming sections with a width of up to 45 cm which are connected by welding collectors. The working pressure is also 10 atmospheres, and the temperature is 120 degrees.
Bimetal radiators
Already from the name it is clear that this type combines the advantages of both materials. The inner shell directly in contact with water is made of steel and coated on top with a layer of aluminum. Because of this, radiators have excellent heat dissipation, low weight and aesthetically pleasing look.
 The system of bimetallic radiators is such that a coolant (mainly water) is supplied through the steel core and then heat is transferred already through the aluminum plates, heating the room. The heat transfer in such structures reaches 170-190 watts.
The system of bimetallic radiators is such that a coolant (mainly water) is supplied through the steel core and then heat is transferred already through the aluminum plates, heating the room. The heat transfer in such structures reaches 170-190 watts.
Operating pressure from 20 to 40 atmospheres, which will significantly increase the durability of the radiator. Of course, the price is higher than a regular steel or aluminum radiator, but it justifies itself.
Cast Iron Radiators
Probably the most common type of radiator to date. Partly due to the fact that almost everywhere where the batteries have not changed for a long time, there are cast-iron. This oldest type of radiator is also the most reliable, with an average life of 50 years.
Significant minus appeared after the distribution of individual heating systems with automation. The huge inertness of cast-iron radiators is incompatible with modern electronics.
But a great advantage over other types of radiators is the absolute corrosion resistance. They are also insensitive to seasonal water spills.
Speaking about the inertness of cast-iron radiators as a bad side in terms of adjusting the temperature in the room, do not forget that this has its own plus.When other types of radiators turn off, they immediately cool down, while the cast-iron still radiates heat.
Another plus, which many consider a minus: slow air heating and section power of about 100 watts, which is 1.5 times less than other radiators. Here is your focus. The fact is that cast iron, unlike other radiators, have a radiation type of heating. This completely compensates for the shortcomings, as walls and objects, which themselves begin to radiate heat, also heat up from cast-iron radiators.
The weight of the cast-iron radiator is the largest of all (one empty section weighs 5-6 kg), but this is not a very significant minus. Another drawback was the appearance of standard radiators. But with the development of technology today, beautiful radiators are created that can be equated with works of art. Well, such a thing is not cheap, so the choice is yours.
Towel warmers
 A special kind of bathroom heaters, the name of which speaks for itself. Towel dryers can be divided into 4 groups:
A special kind of bathroom heaters, the name of which speaks for itself. Towel dryers can be divided into 4 groups:
- Standard - the shape of the letter "P" and "M" with a heat transfer coefficient of 0.6 kW;
- Upgraded - an analogue of the previous ones, with additional sections on each pipe;
- Elegant - differ in heat transfer up to 2.1 kW and a variety of forms;
- With a double heat exchanger - the feature here is that the stainless steel pipe is separated from the design of the heated towel rail and mounted in a riser with hot water, which increases its circulation to the system.

 Heated towel rails are made of stainless steel, ordinary steel and non-ferrous metals, the heat transfer of the latter is the highest. When buying, pay attention to such indicators as:
Heated towel rails are made of stainless steel, ordinary steel and non-ferrous metals, the heat transfer of the latter is the highest. When buying, pay attention to such indicators as:
- Permissible pressure;
- Pipe coating;
- No seams on the pipe (less risk of leakage over time);
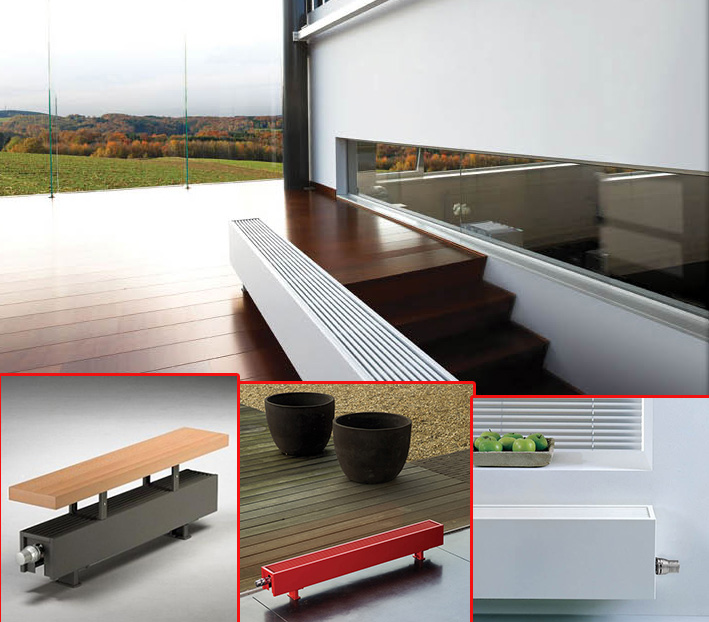
Skirting radiators
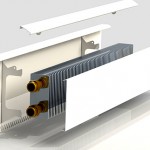 Technology does not stand still, and plinth heating is becoming more and more popular today. There are two types - electrical and water.
Technology does not stand still, and plinth heating is becoming more and more popular today. There are two types - electrical and water.
 Water type consists of parts such as a radiator block, a manifold part and plastic tubes. The principle of operation is based on the law of physics on the attraction of an air stream to nearby surfaces. The air is heated in the plinth radiator in a convective way. He goes into the slot at the bottom skirting boards, heats up and exits through the upper slot, rising along the wall. Thus, some time after turning on the heating, you will get heated walls, which themselves will radiate heat into the room.
Water type consists of parts such as a radiator block, a manifold part and plastic tubes. The principle of operation is based on the law of physics on the attraction of an air stream to nearby surfaces. The air is heated in the plinth radiator in a convective way. He goes into the slot at the bottom skirting boards, heats up and exits through the upper slot, rising along the wall. Thus, some time after turning on the heating, you will get heated walls, which themselves will radiate heat into the room.
The design of the convector uses aluminum and copper, which have excellent heat transfer. Thus, at the working temperature of the baseboard convector 40 °, the walls are heated to 37 °.
Of the benefits such heaters can be distinguished:
- Uniform room heating;
- The problem of moisture on the walls disappears, leading to fungus and mold;
- Small size and aesthetics of the radiator, as well as ease of installation and repair in any room;
- Ability to connect automation;
- Heating to a temperature comfortable for the body;
- Lack of accumulation of warm air masses under the ceiling;
Of the disadvantages the price is allocated - 3000 rubles per 1 meter, the maximum length is only 15 meters and the most problematic is the need for free space that is not obstructed by furniture and other items.
Types of pipes
A very important element in the installation process is the correct pipe selection. There are such varieties as:
- Steel pipes;
- Copper pipes;
- Stainless steel pipes;
- Plastic pipes;
In most cases, all of these types are suitable for your heating system. But there are still cases when some are better and others worse in certain situations. Below we will consider each view in detail.
Steel pipes
This type of pipe is very durable but, despite this, has some flexibility. That allows them to bend, cut and weld.Of the strengths of steel pipes is a slight expansion under the influence of high temperatures, so they can be laid in concrete.
There are 3 types of these pipes - soldered, sutured, seamless. For home heating, the best option would, of course, be seamless, the risk of leakage of which is several times less. Diameter is from 10 to 25 mm.
Of the minuses of these pipes The following can be distinguished:
- Low resistance to hostile environment in comparison with other pipes; 6-7 years - the pipe will last so long before corrosion begins.
- It does not withstand pressure surges;
- Outwardly very poorly combined with the interior of the room;
- High price;
- Low bandwidth
There is an important point to be aware of when buying steel pipes. They are sometimes coated with zinc to avoid corrosion. In such cases, never use welding to join pipes. The zinc coating will simply burn out, and the welding spot will turn into the weakest link in the heating system.
Copper pipes
The first and most important quality of copper pipes is that they are almost resistant to corrosion. The only thing that can seriously harm copper pipes is a galvanic couple formed as a result of a chemical reaction with other metals. Therefore, you need to carefully monitor what radiators are you going to install. In some cases, manufacturers can cover the pipes with a layer of polyethylene, which improves the appearance and protects against external moisture and condensation.
Copper pipes with a diameter of 10-54 mm are produced. There are two types - soft and hard. Of the other advantages, it is worth noting the operating temperature limits from -200 to + 200 ° and the bactericidal effect. Copper pipes better withstand pressure surges, and the service life is up to 100 years. The price of course is far from average and high thermal conductivity is also a significant minus.
There are 3 ways to connect pipes:
- Coupling;
- Threading;
- Adhesion;
Stainless steel pipes
Another type of pipe, characterized by high resistance to any kind of corrosion. There are two types: seamless and electrowelded. The former come in diameters of 5 - 126 mm, the latter - 6 - 1420 mm. As in previous cases, it is recommended to use a seamless option.
Pros:
- High bandwidth;
- Resistance to pressure surges;
- The service life reaches 100 years.
A significant minus for most buyers is the high price. Yes, and high thermal conductivity will adversely affect the temperature of the heater. Connect stainless steel pipes in the same way using couplings, threads or welding.
Plastic pipes
One of the most popular pipes today is plastic. The most important advantage of these pipes, which make them so popular, is their absolute resistance to favorite types of corrosion. Plastic pipes will last at least 50 years. An important point is the absence of noise from the flow of water through them.
An important factor is the lowest thermal conductivity among all types of pipes. This will save some heat. Also, plastic pipes withstand a lot of pressure and its jumps, they are the cheapest and easiest to install. Below we consider the types of plastic pipes.
Plastic pipes
The design of these pipes is the outer and inner layer of plastic and aluminum foil with a thickness of 0.2-0.3 mm between them. The polyethylene itself is very durable, has a roughness of about 0.004, a break border of 70 bar, and an operating temperature of up to 95 °.
The aluminum ball plays a very important role in the construction of the pipe. Thin and elastic, it is at the same time durable, prevents pipe deformation and elongation when exposed to temperature.
Plastic pipes withstand pressure up to 10 bar at 95 degrees temperature. For some time they can tolerate a temperature increase of up to 130 °. The service life of pipes reaches 50 years.
Polyethylene pipes
Polyethylene pipes are environmentally friendly, are also resistant to corrosion and resistant to abrasion. Also, the advantages include light weight, strength and flexibility, ease of installation.
- Features of polyethylene pipes:
- The term of operation is 60-100 years;
- Withstand very low temperatures;
- They withstand pressure drops and mechanical stress, due to which they are used in seismically active zones;
- Working pressure at 0-25 ° reaches 25 bar;
- A short period of time capable of working at a temperature of 100 °;
Polypropylene pipes
This species is more rigid than the rest, because they are bent under a large radius. Also for these pipes you need more corner fittings. The installation process itself is more time-consuming and costly than the same metal-plastic pipes.
Specifications:
- Working temperature = 70 °;
- Working pressure 10-25 bar;
- The term of service is 50 years;
PVC (polyvinyl chloride) pipes
PVC pipes are made from thermoplastic polymer. The operating temperature of these pipes is the lowest of the plastic family - 70-90 °. The peculiarity of PVC pipes is chemical resistance and low combustibility. Like other plastic pipes, they are characterized by corrosion resistance, strength, low price, high working pressure.
Heating system installation
This process involves shutting down and dismantling old radiators and pipes. Selection of new radiators by calculating and determining the type of pipes to be used in the heating system. Soldering pipes and fixing pipes and radiators to the walls. Connection of all elements of the system and connection to a heat source.
Small calculations
To choose the right radiators for your heating system, you must at least determine the place where it will be mounted, the number of windows and the number of external walls.
To heat a room with 1 window and 1 external wall, up to 3 meters high, you need about 100 watts. Next, just add power based on the following calculations:
- +1 external wall + 20% to power;
- +1 external wall and 1 window + 30% to power;
- +1 window facing north + 10% to capacity;
- If the radiator is closed by the panel, then + 15%, and if it is in a niche, then + 5% to power;
When summarizing several points, additional percentages of power are also summed.
The approximate dimensions of the radiator are determined using some rules:
The distance from the window sill to the radiator is at least 10 cm, from the radiator to the ceiling 6 cm. The width of the radiator should occupy at least half the width of the window, and preferably 75%.
Shutdown of water supply
Very often there are problems with disconnecting the riser, to replace or repair the heating system. The riser is public property. Access to it has a municipal service. If you receive a refusal to disconnect the riser during work, be sure to request that the refusal be submitted in writing. Then you will be what will appeal to the court. Everyone understands this perfectly and in most cases does not reach this point. The management company is simply required to comply with the requirements of the tenant. But this service (shutdown of a riser) is paid. The price varies from 500 to 1500 rubles per hour in different areas.
There is another pitfall in the process of replacement or repair - neighbors. There are situations when access to neighboring apartments is needed and “friendly” neighbors refuse to provide it. Of course, this is their private territory, but there are standards (housing code, articles 3, 8, 36, 37, 129), according to which permanent access to the public riser can be provided even without their consent. Therefore, you again have the opportunity to go to court. Having well explained this to the neighbors, you can do just talking.
Radiator Preparation
Before mounting the radiator, you need to pack it. This is the name of the installation process of plugs, fittings and a Mayevsky tap in the radiator holes.
To get started, take the foots and screw in 4 places. Usually there are 2 with the left and 2 with the right thread, we tighten them with an adjustable wrench with medium effort. They already come with a silicone gasket, so it is unnecessary to seal them with anything else. Next, we find the front side of the radiator and determine by the old radiator which side the eyeliner is on.For example, on the left. Then we screw in the plug on the bottom right, and the Mayevsky crane on top. It is needed to remove air when filling the radiator with water.
Now on the left side, bottom and top, we install 2 fittings with an external thread and crimp for supplying pipes to the radiator. We take the fum tape, wrap it on the external thread of the fitting and apply a paste to seal the threaded joints. The paste layer should be approximately 2-3 mm. This paste dries during the cold season during the heating season and additionally makes the connection more reliable. We put the fittings on the thread and tighten with an adjustable wrench until the twist starts to unscrew, then with the same wrench we pull the twist back. Remove excess paste with a towel. Actually on this, the preparation of the radiator is completed.
Removing the old heating system
After the water in the riser is shut off, you need to drain the water from the radiators. To do this, attach the hose to the drain valve of the radiator, and release the other end into the street through the balcony or into the sewer. Under the place where the hose and valve are connected, substitute an empty container in case of leakage. If there are air taps in the system, open them to speed up the process of draining the water. Then you can proceed to the next step.
Using a grinder, make two cuts on the pipe you plan to replace. Incisions are made at a distance of 5-15 cm from each other, deep, almost completely cutting the pipe. Now we take the gas key and, clamping the space between the cuts, we break out this section. It is not necessary to completely cut the pipe, this is fraught with jamming of the disc of the grinder and is even traumatic.
We remove the largest possible section of the old pipe. It all depends on the specific situation. In most cases, this is the distance from the radiator to the wiring in the riser or to the swivel fitting or to the cork of the adjacent radiator. Next, remove the old radiator from the wall. Here either we remove from the loops, or together with them if they have “grown together” for a long time. If the loops remained in the wall, they can be unscrewed, but sometimes they are very firmly held then just saw off these loops with a grinder near the wall itself.
Next, using a gas wrench, unscrew the remaining parts of the old pipes. This must be done carefully so as not to damage or disturb the rest of the pipes and connections. If the thread does not lend itself, you can knock on it. In especially severe cases, heating the problem area with a blowtorch helps.
Now you can proceed with the installation of the radiator itself.
Radiator mounting
We take the level to make marks. We put it against the wall opposite the thread of the eyeliner, from where a piece of the old pipe was twisted. Mark at the middle of the feed and return holes. In this way we reach the radiator holes. Now you need to substitute something under the radiator so that the middle of its threaded holes coincides with the marks, and makes serifs on the wall for fasteners.
Next, we drill holes for dowels and screw in the hooks that will hold our radiator in weight. You hang up the radiator and use the level to check how smoothly it sat in place.
Piping assembly
So far, the work with the radiator is finished. We pass to eyeliners from the riser. They need to screw in two ball valves. To do this, the tap must be with an external thread on one side and an internal thread on the other. If you have a faucet with two internal ones, then simply screw on one side a special nipple. You select all diameters based on those that are already in the eyeliners. Usually it is ¾ inch or 20 mm. You need to screw the taps by wrapping the fum tape with the place of thread and greasing with paste; You can also use tow and flax. Now put the tap on the thread and tighten with an adjustable wrench, remove the protruding paste residue with a towel.
Tip: try to screw in the valves so that the valve handle is at the bottom. This will avoid accidentally opening or closing the tap if you hook them with anything. It is very important if there are children in the house.
The diameters of the pipes in most cases take 20 mm for the wiring of apartment heating and 25-32 mm for the riser.
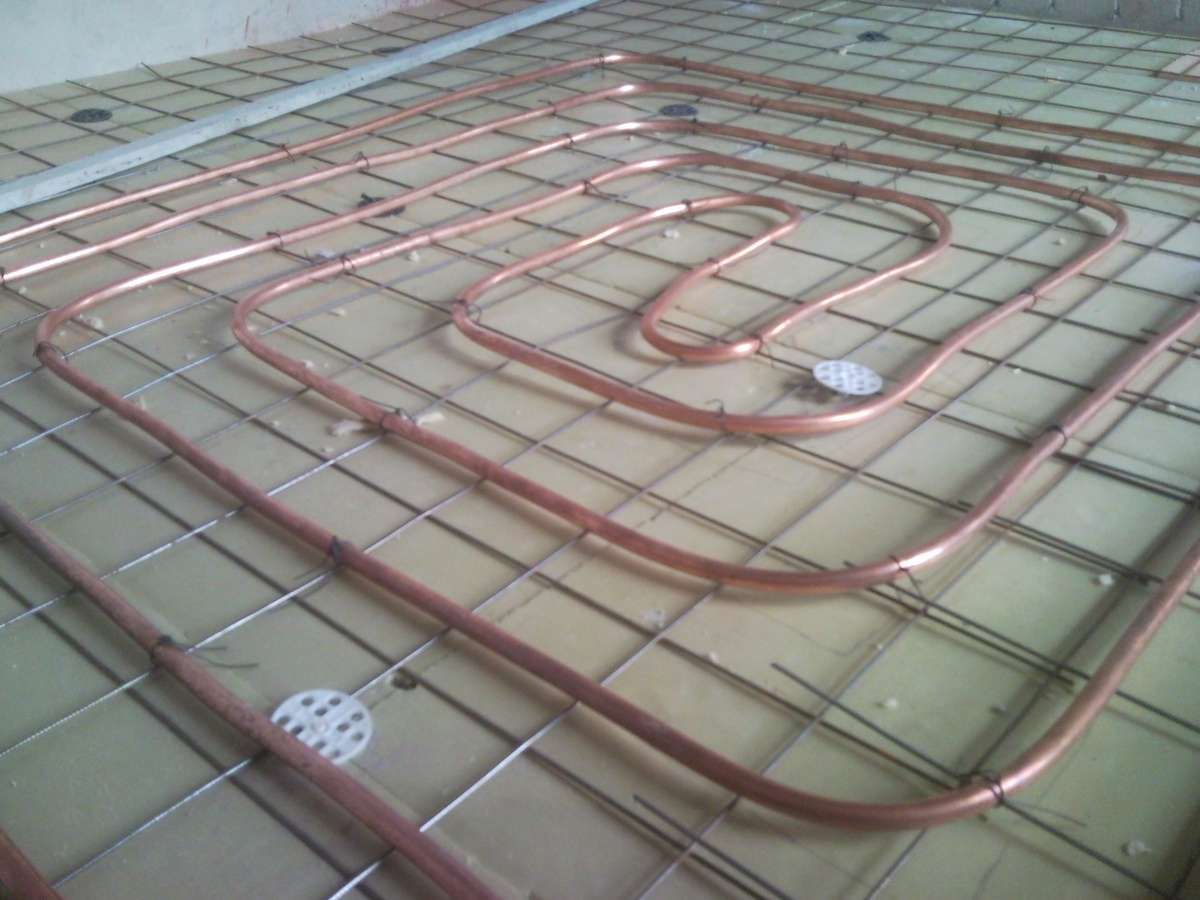
We take adapter fittings for soldering a copper pipe or plastic and screw it into the wiring. It all depends on what type of pipes you have chosen. Next, we consider in detail 2 ways of installing a pipeline for copper and plastic pipes.
Copper pipes
If there are copper pipes, screw the fittings just to try on, then unscrew them back. Measure the desired pipe length to the swivel fitting. Take the pipe and cut off the desired piece. After that, we clean the edges with the same grinder. Place it lying down and drive the end of the tube in a rotating circle. Prepare a blowtorch. It is advisable with a narrow end of the flame, but these are a little more expensive, so if there is no possibility, then you can do the simplest for 150-200 rubles. Prepare the solder. Solder the adapter fitting (from the riser wiring) to the tube separately, and then screw the fitting with the tube into place. If you do the opposite, there is a risk of burning the valve in the ball valve.
The end of the tube to be soldered must be cleaned. For this, ordinary sandpaper is suitable, you just need to wrap the tube with it and rotate it in one or different directions until the end becomes noticeably lighter. Next, using the hedgehog, we clean the inside of the fitting. Lubricate the end of the flux tube with paste and insert into the fitting until it stops. We remove excess paste with a towel. Now we heat the soldering place with a soldering iron and for 30-40 seconds (the paste begins to turn white) and lower the solder. We repeat the same thing with another tube (we need 2 of them) and wait until it cools down.

 Next, screw the fittings into the feed and return, pre-wrapping them with fum tape and coated with paste to seal the threaded joints. Next, we fit the swivel fittings onto the tubes and measure the length of the pipe segments we need, cut and insert into the same swivel fittings, and we swivel the fittings again at the other ends and measure the remaining distance.
Next, screw the fittings into the feed and return, pre-wrapping them with fum tape and coated with paste to seal the threaded joints. Next, we fit the swivel fittings onto the tubes and measure the length of the pipe segments we need, cut and insert into the same swivel fittings, and we swivel the fittings again at the other ends and measure the remaining distance.

 Now we solder in the same way, we just start from the radiator. First, insert the tubes into the radiator and fix with clamps. In these places it is better to use this type of connection, since in the future it may be necessary to remove the radiator. Next is the soldering of all the connections in turn. Last, we weld the tube from the riser to the swivel fitting, having previously connected the entire system together and adjusted it by moving the radiator left-right. That's all, the heating system using copper pipes is ready.
Now we solder in the same way, we just start from the radiator. First, insert the tubes into the radiator and fix with clamps. In these places it is better to use this type of connection, since in the future it may be necessary to remove the radiator. Next is the soldering of all the connections in turn. Last, we weld the tube from the riser to the swivel fitting, having previously connected the entire system together and adjusted it by moving the radiator left-right. That's all, the heating system using copper pipes is ready.
Plastic pipes
Plastic pipes noticeably expand when heated, therefore they cannot be cemented in the ceiling or walls, and during installation you need to leave a little space for their “movement”.
By analogy with the previous option, all sections are measured and pipes are cut. Please note that for soldering plastic pipes, about 15 mm will go inside the fitting. Here we need a soldering iron with removable nozzles. Turn on the device and wait until it warms up completely (the indicator lights up in red). Next, the tube is inserted into the clutch of the soldering iron, and the fitting is put on the nozzle-mandrel.
Pipe heating time:
- 20 mm - 4-5 seconds;
- 25 mm - 7-8 seconds;
- 32 mm - 10-12 seconds;
At a low temperature in the room where the work is carried out (+ 5 ° С and below), it is necessary to increase the heating time by 50%. Pipe manufacturers recommend a unit temperature of 250-300 ° C. It is undesirable to solder two tubes of different materials and manufacturers. If it is slightly heated, then the connection will not be strong, and if it is overheated, then passability can be significantly reduced or even the tube can completely stick together. The surfaces themselves that are soldered should be beaten dry and clean.
After sustaining both halves of the specified time, pull out from the apparatus and connect together, then hold motionless for 5-6 seconds. To avoid deflection when welding perpendicular or angular parts, make notches on both halves.At the same time, back off at least 15 mm so that the notches are visible when connecting the pipes.
Always draw a schematic diagram of pipes and elbows where you will mount them (on the wall or floor). It is not always necessary to weld elements in a strict order; it is better to assemble several large segments and then combine them into a whole system.
If the sections are long and the system itself comes out large, then use special fasteners for plastic pipes (if mounting is done on the wall). This point should be determined before starting the pipe soldering, in order to mark and drill the places for dowels in the wall.







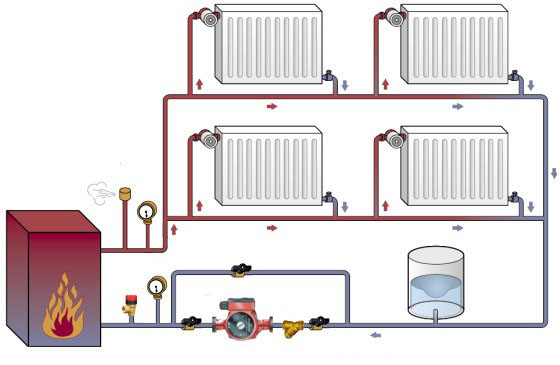

“To heat a room with 1 window and 1 external wall, up to 3 meters high, you need about 100 watts. Then just add power based on the following calculations: "
I would also take into account losses on infiltration and on the power that will heat rooms without radiators, such as a corridor, a / c, etc.