What foundation to choose for the garage: 7 tips
The garage must be reliable, sturdy, protect the car from external factors, stable, convenient enough so that it can carry out auto repair on its own. Its durability largely depends on the type of substrate. What foundation to choose for the garage, you must decide first.

Structures such as a garage shell or a metal box (box), as a rule, do not need a foundation. Further in the article we will talk about the fundamental support for solid, major garages, which can be made in one or two floors, equipped with a viewing hole and other additional elements.
Dependence of the choice of the type of foundation on the ground
What are the main factors affecting the right choice of foundation? It:
- Used building material.
- The size of the garage, its configuration and estimated weight.
- Type of soil.
- Soil water level as well as seasonal rainfall.
- Depth of freezing soil.
Geological analysis of the soil is a mandatory preliminary step that must be carried out before start of construction. In the course of the study, the strength of the soil, the probability of subsidence and expansion of the earthen coma, and resistance to displacement are established. If, for example,
- Groundwater flows above freezing - it will be necessary to construct drainage gutters, drainage ditches to artificially drain groundwater.
- The composition of the soil is completely unsuitable for the construction of the foundation - then improve its quality and structure by adding sand, gravel, it is possible to add man-made compacted layer, which can be obtained by pneumatic ramming, cam rolling and other methods.
- Soil problematic with a high degree of humidity (clay soil) - with a minimum error, calculate the depth of the base regarding the depth of freezing of the soil.
To choose the most suitable material for the construction of the garage, determine the type of foundation, its technical characteristics, you need to familiarize yourself with the types of soils.
Soils are:
- Sand. Differ in small depth of freezing. The larger grains of sand, the higher the load can withstand the soil.
- Clayey. A feature of heaving soils is the large depth of possible freezing and instability with a large amount of moisture.
- Sandy loam and loam. The main components are sand, clay. When severe frosts are subject to a strong change in volume
- Rocky. They do not freeze, do not shrink, do not have cracks and splits, the soil is a continuous monolith.
- Cartilaginous. Not affected by subzero temperatures, deformation, erosion or subsidence. Represented not in monoliths, but in stone pieces.
- Peat bogs. More than 50% are composed of organic substances. This type may include clay, sand, and silty clay soils with an organic content of up to 20%.
- Gravel. The base is gravel, the freezing depth is low, the possibility of deformation is insignificant.

Based on the type of soil, not only type of future foundationbut also its depth. Because when on the site:
- Rocky rocks, it may be enough to make a concrete screed.
- Gravel, the depth will be 50 cm.
- Sandy soil - depth varies from 40 to 80 cm.
- Loamy soil - get ready for a trench, foundation pit or wells more than 1.5 m deep.
It is important to consider that the foundation depth line should be located at least 50 cm above the level of soil water
Today, the most common are several types of garage foundations. To choose the most suitable option for a particular type of soil, it is necessary to take into account the architectural features of the building, as well as the financial capabilities of the car owner.
Garage foundation strip
The design is a reinforced concrete tape running along the entire perimeter of the garage, with the same cross section (rectangle) along the entire length.
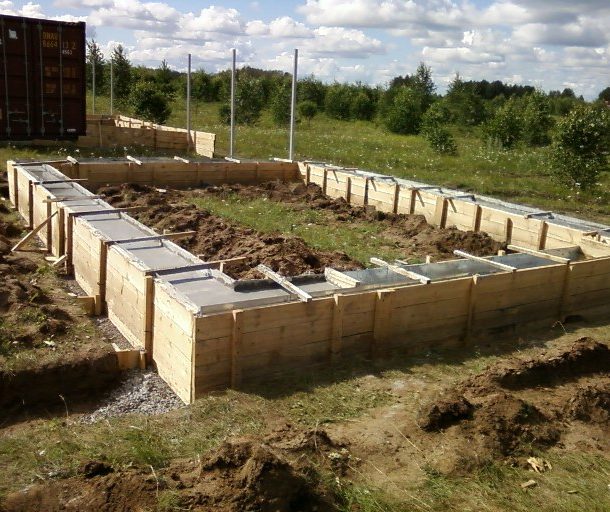

TO the benefits Such grounds include:
- Versatility, since this type of foundation is suitable for almost any type of soil.
- Possibility to equip a basement or a viewing hole in the garage.
- Use in construction: buta, butobeton, concrete, bricksreinforced concrete.
- Suitability for buildings with brick, concrete, stone walls.
TO disadvantages significant earthworks are often referred, but they more than justify themselves, since a correctly made construction will be strong, durable, and can stand for more than 100 years.
Monolithic and prefabricated strip foundation
Strip foundations are:
- monolithic (jellied, seamless)
- national teams.
For prefabricated base you will need ready-made blocks, pillows for them, which during the work will be held together cement mortar. Reinforced concrete blocks are installed in a prepared trench with an organized sand cushion. In some cases, the presence of the latter is not necessary, it will be enough just to level and tamp the existing soil well. The advantages of using fundamental blocks:
- Installation speed.
- Factory quality without distortions, valve breaks, internal defects.
- Lack of a technological break before the erection of walls.
- Stability and durability.
On the other hand, it’s:
- The presence of connecting seams.
- The possibility of seepage of water or rupture of the base at the junctions of FBS or FL blocks.
- Discomforts when assembling a structure with complex geometry.
- Attraction for laying heavy equipment, which means an increase in the total price of the foundation.
Although manual laying of blocks for the foundation is possible. It can be products from classical concrete (weight - 31.7 kg one piece, size - 20x20x40) or from expanded clay concrete (weight - 28 kg)
Monolithic base for the garage is the most popular in individual construction. Despite the complexity of the process, all work can be done independently. Before the beginning of active actions, it is necessary to carry out calculations, determine the width and depth of the structure. As a rule, the width of the foundation is 30% greater than the thickness of the walls of the garage, but the depth is calculated relative to the depth of freezing of the soil plus 20%. Also, one should not forget that the base of the structure should rise 20-30 cm above the ground level.
Types of foundation by degree of capital
By degree of capital strip seamless foundations are divided into:
1. Unfinished
Arranged on the surface. Perhaps building on rocky soils that are not subject to erosion, expansion, deformation.
2. Shallowly buried
They are laid at a depth of 50-70 cm on such soils as:
- Coarse pebble - sand, pebbles, small rocks. Differs in high durability therefore it is not deformed.
- Coarse gravel - a mixture of coarse rock, pebbles, sand and gravel. The soil is not deformed, but shifts are possible.
- Cartilaginous - stone fragments and gravel. Very high strength is characteristic, without possible erosion and squeezing.
- Large sandy ones - have an insignificant degree of freezing, weakly compress, pass water well.
- Medium-sized sand - they freeze slightly, do not retain moisture, and have a strong compaction under load.
3. In-depth.
Deep structures are relevant in areas with:
- High humidity.
- Shallow freezing depth.
- Foamy soils: large and medium sized sands, cartilaginous, coarse, loam.
Tape construction - construction stages
To install a monolithic foundation, you will need:
- Sand and gravel mixture for pillows.
- Waterproofing materials.
- Formwork (you can use boards, sheets of tin, plywood, polymeric materials).
- Fittings.
- Concrete mix.
When a drawing is made indicating the configuration of the garage, all necessary sizes, an analysis of the soil is carried out, calculations are made to deepen the foundation, building materials are prepared, you can begin to lay the foundation. The algorithm of actions is as follows:
- Excavation. The trench digs deeper by 30-50 cm than the foundation depth is laid in the project. These centimeters will be filled with a well-compacted sand-gravel or sand cushion, which is needed to make the bottom of the trench more even and to perform the function of additional heat and waterproofing. In addition, sand will serve as a drainage function.
- First layer of solution. In many cases, the pillow is poured with a layer of "concrete", the thickness of which is 10-15 cm. To strengthen concrete preparation, you can put reinforcing mesh.
- We install the formwork. Use purchased or home-made formwork, removable and non-removable. In the absence of professional skills, it is worth acquiring a ready-made design in order to exclude possible irregularities or miscalculations in size. For removable formwork fit: wide boards of small thickness, slate sheets and chipboard, thick plywood, metal sheets, polystyrene foam (polystyrene). The fixed row includes: arbolite (hollow panels made of cement and wood chips), glass magnesite (metal thermoprofile encircled with a glass-magnesium cloth), polystyrene foam blocks, etc. At the same stage, we think over the future laying of communications. The formwork must keep the solution in a specific form, so the main thing is the exact dimensions, high-quality and even fasteners, deviations and distortions are not allowed.
If the site for the construction of the garage is inclined, then the formwork will help to bring the swings (horizontally) into one plane. According to calculations, the formwork at the lowest point is constructed above
- Reinforcement. A mesh of reinforcement serves to strengthen the base of the garage. Smooth reinforcement serves as protection against lateral loads, ribbed from longitudinal ones. The minimum number of vertical rods in the frame is two rows, the number of horizontal rods increases in proportion to the estimated depth, the step is 30 cm.
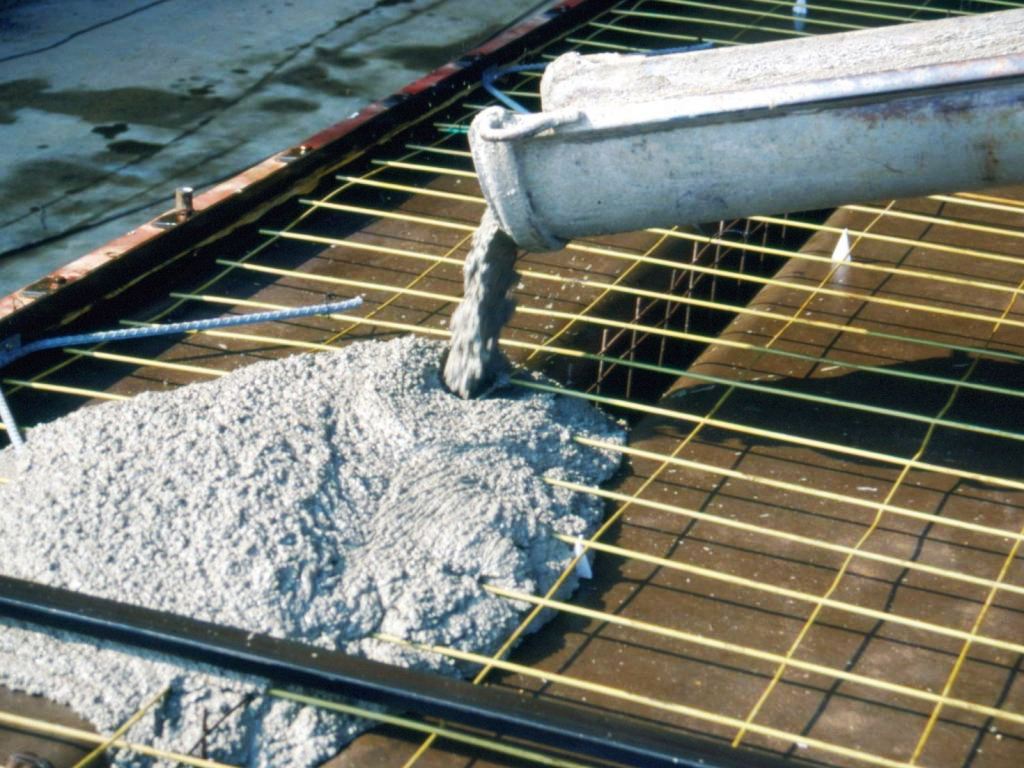
- Concrete pouring. The process can be carried out in one or several stages. When phased pouring, each layer should not exceed 20-30 cm (one dries up - the next one is poured), and time intervals - 12 hours. In the construction, factory-made concrete or concrete mix of our own manufacture is used in compliance with all the necessary proportions of the components. Depending on weather conditions and the time of year, foundation concrete must be protected from precipitation, direct sunlight, and low temperatures.
Important:
- Do not rush, and in the absence of hardening accelerators in the mixture, allow concrete to gain strength in a certain number of days.
- Do not forget about waterproofing, which will protect the garage from fungus and dampness, and the foundation - from destruction.
Floating (slab) foundation for a garage
One of the types of strip foundation. It is stable enough on unreliable heaving soil, clay, marshy terrain, under adverse weather conditions (excessive precipitation), soil vibrations and increased loads.
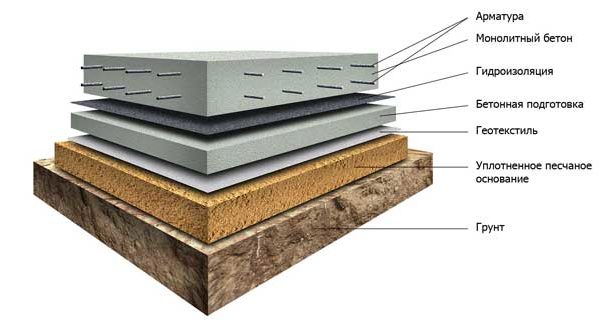
Reinforced concrete recessed slab can be:
- Plain (simple) - perfect for relatively small garages.
- Monolithic trellised (national team) - a little expensive.
- Monolithic reinforced (at the edges) or with longitudinal stiffeners - the optimal ratio of price and strength.
TO the benefits this type of foundation can be attributed to:
- Simple technology to perform.
- An opportunity to carry out work independently.
- Good bearing capacity.
- Strength and stability, because the base is a rigid monolithic platform.
- The possibility of organizing slabs on complex types of soils, without applying major work with the ground.
- Simultaneous performance of the functions of the bearing base and the floor of the garage.
We carry out construction work in the following order:
- We apply dimensional marking and dig a pit to the desired depth, taking into account the part above the ground (about 50 cm). The bottom can be laid geotextile.
- Fall asleep pillow with a layer (up to 20 cm) of crushed stone of medium fraction and sand in the required proportion, we ram it and level it.
- We carry out a concrete coupler (brand M 100) with a thickness of 7 cm and well withstand it (at a temperature of + 20 degrees - 10-15 days).
- We expose the formwork.
If the site is sandy, then the formwork under the brick or iron garage is installed before filling the screed to the entire depth of the pit
- We carry out waterproofing screeds.
- We put a frame of reinforcement, the cross-section of the rods is 8-10 mm, the mesh cell is 30x30 cm or 15-20 cm. The stiffeners require a pitch even less than that indicated. The distance from the edge of the mesh to the concrete surface should not be less than 4 cm.
- Fill concrete. We carry out the procedure in one step in full. The plate is covered with plastic wrap and allowed to stand. After 7 days, we remove the formwork, after a month you can proceed with further construction.
A floating foundation is a low-laying design that is rapidly gaining popularity.
Garage column foundation
These designs equip when the use of other foundations is impractical:
- In soils with a high degree of freezing.
- In areas with difficult terrain.
- With poor soil bearing capacity.

The base is a system of wooden, stone, rubble or brick pillars, combined into a single whole. Due to its fragility, despite all kinds of impregnations and waterproofing protectionWood poles are very rarely used today. As for other materials, the supports of them are installed at a distance of 1.2-2.5 m from each other in the most critical places: corners, points of intersection of walls, runs with increased load.
Construction technology
According to the installation technology, it is necessary:
- To drill wells into which to fill a layer of sand and crushed stone pillows.
- In the holes, lower the ruberoid rolled into a roll, asbestos-cement or steel pipe so that their upper edge is 30 cm above the ground level. These materials will serve both as waterproofing and formwork of the posts.
- Amplify reinforcing mesh with a rod cross section of 6 mm - for horizontal, 10-12 mm - for vertical. Now the reinforcement is 20-30 cm higher than the formwork (for a reinforced concrete frame).
- We fill and ram concrete.
We integrate all the columns into one structure using strapping beams, steel channels or concrete grillages. The main thing is that an even plane forms horizontally.
For different materials, the corresponding column sizes are determined:
- for wood - diameter 25-28 cm.
- for reinforced concrete - 25 cm.
- for but concrete - 50-60 cm.
- for bricks - 50-55 cm.
The foundation of the columnar type is reliable, economical and does not require additional work and the cost of waterproofing.
Garage column foundation
The described type of foundation is combined and relevant in the presence of a large amount of groundwater in the ground.

The construction process in many respects coincides with the arrangement of the strip foundation, but there are some new points. The sequence of work is as follows:
- Swarm trench.
- We prepare the holes. Each diameter is from 15 cm, depth is 100-200 cm, the distance between the recesses is not less than 1 m.
- We prepare the holes for pouring concrete mixture: put 10 cm of sand cushion into each, install the formwork from an asbestos-cement pipe or roofing material, put the frame from the reinforcement (metal).
- We carry out work with a trench, as for the tape structure (see the previous paragraph), at the end of which we fill the foundation.
Garage pile foundation
On the site is weak soil, which is easily compressed, or, conversely, too hard, or maybe the depth of the natural base (under the peat bog) is quite large (4-6 m)? Then a pile foundation is installed under the garage.

His advantages:
- The minimum time for all work.
- Possibility of year-round installation.
- Lack of work to level and prepare the soil.
- The degree of deepening of the piles compensates for differences and slopes of the relief.
Piles can be metal, wood, concrete, reinforced concrete; hollow and whole; with a round, rectangular and pyramidal section.
Transfer method as well as load distribution (on the ground) piles are:
- Hanging, as if stuck in a light breed, not reaching a solid base. Basically, such piles at the end have screw threads for strong adhesion to the ground, and for holding and transferring the load they use their entire vertical surface.
- Piles risers (standing, retaining), after passing through weak layers, they reach hard and firmly abut against the base with the ends.
There are piles arrangement methods:
- Clogged. Due to the involvement of special equipment in the installation process and, consequently, the increase in financial costs, this type is used in industrial and civil construction. In fact, the elements of the future foundation "clog" in the literal sense. During installation, a strong compaction of the soil around the pile occurs, which adds to it reliability and stability.
- Stuffed (bored). The arrangement takes place according to a technology identical to the method of installing the column foundation. Wells are drilled on the marked area, which are then poured with concrete. The heads brought to the required height are joined by a connecting frame. In this case, piles can be made reinforced and unreinforced.
- Screw. Elements made of metal with screw blades at the ends allow you to quickly equip the foundation. One of their main advantages is a huge bearing capacity. When equipping the basics pile screwed until it reaches a stable layer. During the movement of the blades, the soil is compacted, becomes strong.
- Multi-turn piles hold fast in the ground, do not roll and do not sag, are reliably protected from corrosion, do not need additional concrete mortar, are installed in any soil directly near the foundations or walls of other buildings. Therefore, foundations with their use today successfully compete with already well-known structures.
What foundation for the garage to choose?
To summarize:
- Swampy soil, permafrost or a high level of groundwater - forget about the viewing hole and basement, choose a slab or pile structure.
- There is no need for a viewing hole - make a slab or strip of slightly shallow foundation.
- Need a basement - only the tape base.
- A plot with a complex terrain - a pile structure with a reinforced concrete grillage is suitable.
- Light weight garage from foam blocks - the best choice would be a concrete monolithic slab with a depression of 40-50 cm.
- Frame garage - taking into account the soil and water level, 3 main types of foundation are suitable: strip, pile, slab.
- Small brick house for one car - organize a reinforced monolithic tape, deepened to 80 cm.
- Iron garage - pay attention to the concrete monolithic reinforced slab.
- As alternative materials for the foundation, you can use: sleepers, road plates.












The foundation is the foundation. And he really needs to pay special attention. Thanks for the tips!