7 tips for choosing a power cable for a private house
It is difficult to imagine the life of a modern person without electricity. Most of the household and work processes without it would be very difficult or impossible to complete. To provide all of us with electricity, powerful power plants are being built and kilometers of power lines are being laid. To connect your own home to electricity, the only thing left is small - to choose a power cable for a private house, electricity will flow through it to the final consumer. Electricity is not only a blessing, but also a source of increased danger, so the selection process should be given maximum attention. We deal with the main points.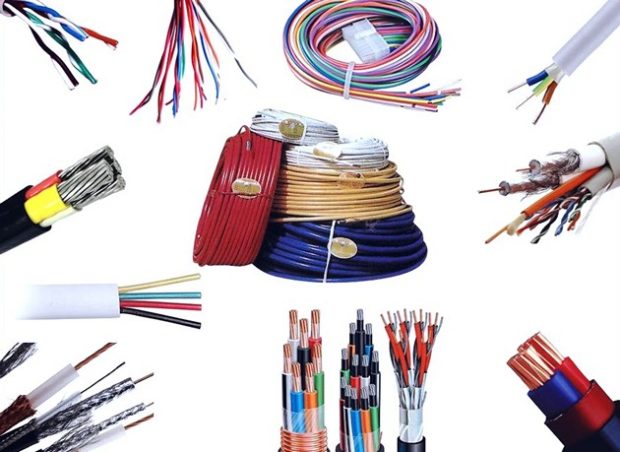
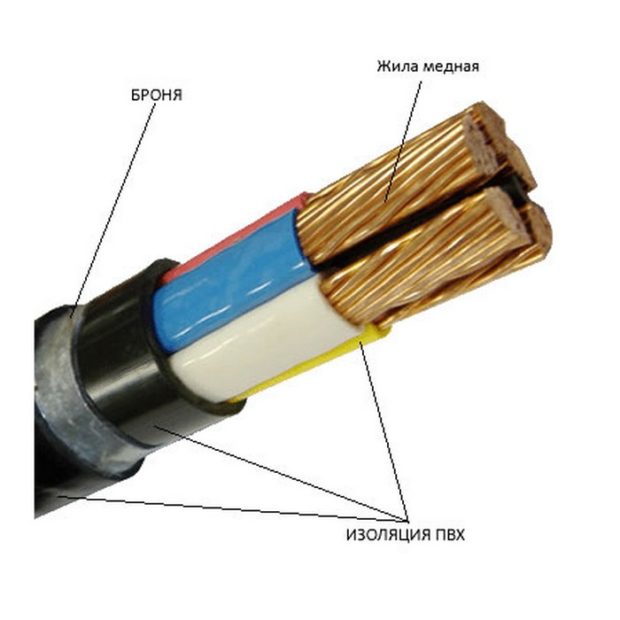
No. 1. Power cable structure
Low voltage power cables are rated for 10-35 kV, and high voltage cables are designed for 110-750 kV and more. It is clear that with such a range of possible values, the cable cannot have a unified structure, but there are some common elements in all samples. We are talking about conductive conductors (TPA), their protective sheath and general (zone) insulation. Usually, cable structure much more complex and includes a lot of additional elements.
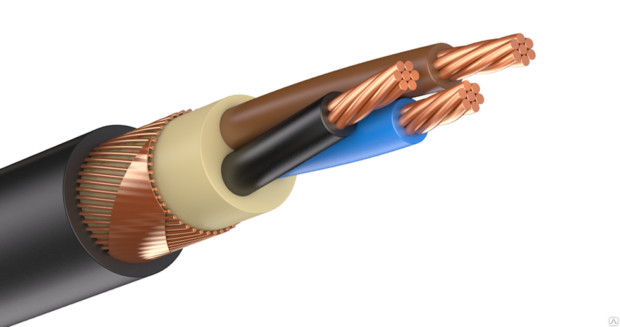
Usually in a cable from 3 to 5 conductive conductors, each of them can be made of one (monolithic, single-wire cables) or several interwoven wires (multi-wire). Between the wires in one core there is no insulation. The more wires in one core, the more flexible the cable will be, which is important for some sections.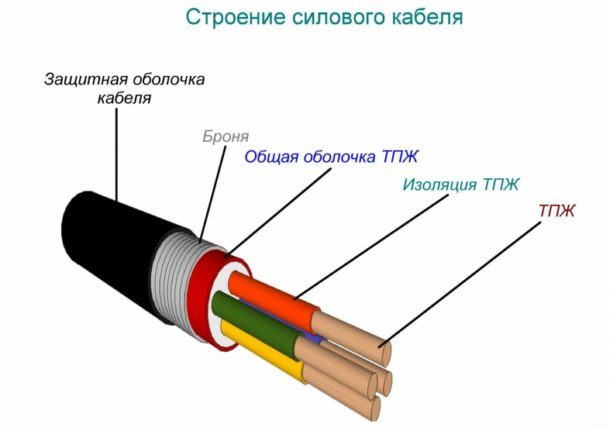
Cores are imprisoned in individual isolationare in the cable in parallel or in twisted form. They are made of aluminum or copper, the second option is better in all respects. Aluminum conductors with a cross-sectional area of less than 35 square meters. mm and copper with an area of up to 16 square meters. mm are made from one wire. With a cross-sectional area of 300-800 square meters. mm for aluminum conductors and 120-800 sq. mm for copper use several wires. For intermediate values, both monowire and stranded wires can be used. Also, a cable often contains a zero core and a ground wire. The cross-sectional area of the zero core is less than current-carrying.
Cores are imprisoned in general isolation, a screen can be placed on top of it, which additionally strengthens the insulation, but its main task is to attenuate electromagnetic rays. If the cable is laid in difficult conditions, then armor or braid can be used.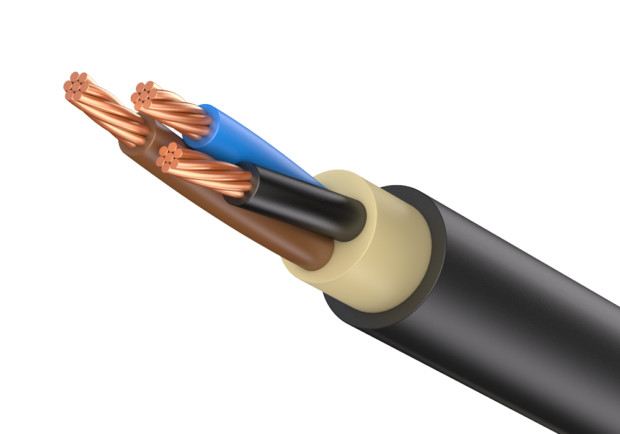
The structure of the cable, the materials used for insulation and protection differ significantly depending on how the installation is carried out - in the ground, indoors, outdoors. The cross section of the cable will depend on the power consumption of electrical appliances in the house. All these parameters are selected and calculated individually. General requirements remain maximum quality, durability and reliability. There is probably no reason to explain what can happen when using a low-quality cable. To be sure of your own safety and comfort, use the products of trusted manufacturers. RKB company has already made such a selection for us - the supplier offers the widest range of cable products from reputed manufacturers.Due to the presence of numerous branches and own warehouses, delivery is carried out in an extremely short time. In which case, employees will help you choose the cable of the required brand.
No. 2. Core material
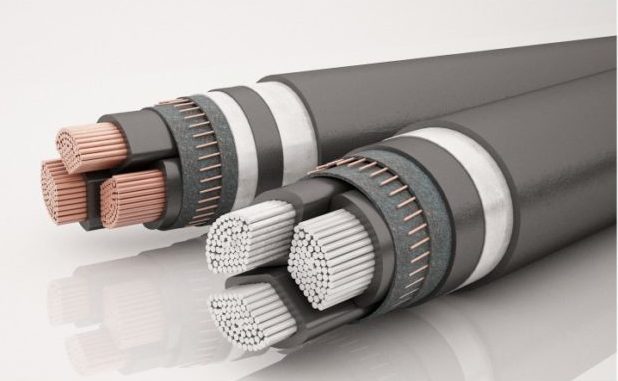
The cores are made of aluminum or copper.
The advantages of copper conductors should include:
- higher current conductivity (1.7 times higher) and lower resistance than aluminum. With the same cross section, the copper core can withstand more severe loads;
- higher corrosion resistance than aluminum;
- higher strength;
- the higher ductility of copper allows it to remain intact even with severe bends. Even single-core wires can withstand significant deformations. What can we say about stranded;
- simplicity of soldering and welding - no additional materials are required.
The main minus cable with copper conductors - its price. Moreover, copper is almost 3 times heavier than aluminum. Despite these shortcomings, copper is considered a more acceptable option, and the high price more than pays for its durability and reliability.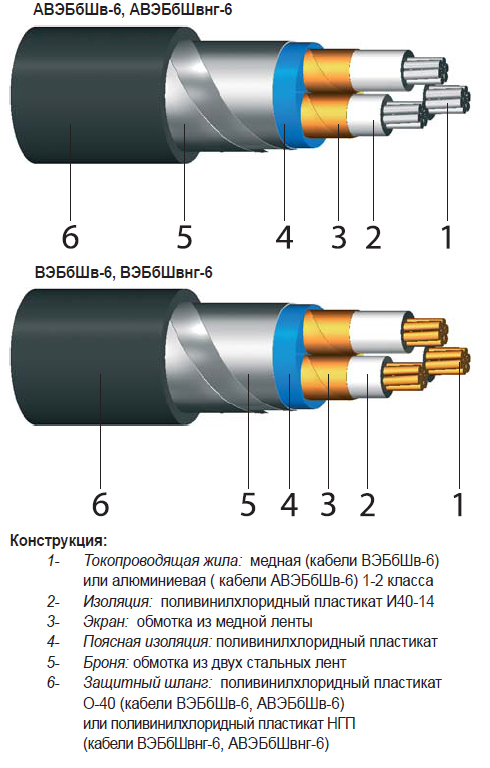
Aluminum until recently, was a favorite in the field of cable and wire manufacturing. Among all metals, it is the fourth in electrical conductivity. Aluminum yields to gold, silver and copper.
The advantages of aluminum conductors include:
- low cost;
- minimum weight;
- chemical resistance.
This was enough for aluminum to be massively used for electrification. Today, the rules of PUE in the home forbidden to use a cable with aluminum conductors with a cross section of less than 16 square meters. mm, since it does not have sufficient flexibility so that it can be bent at right angles. When in contact with air, aluminum forms a refractory, non-conductive current film that can heat to such an extent that it begins to spark. The low yield stress leads to the fact that over time fastening with screw clamps can weaken. Power cable with conductors over 16 sq. mm is more flexible, but it is used only when you need to save. The service life is shorter than that of analogs with copper conductors.
You cannot connect copper and aluminum directly - in such a pair, aluminum will gradually begin to oxidize.
No. 3. Type of insulation
In power cables, each core receives individual insulation, plus there is also general, or belt insulation. Internal insulation is necessary to prevent contact between the cores; the outer provides additional protection and holds all cores together.
The choice of insulation material depends on how the cable is used. It is necessary to evaluate the following parameters:
- mechanical strength is especially important when it comes to overhead cable installation;
- resistance to ultraviolet rays. There are materials that gradually become brittle when exposed to the sun. Such cables without additional protection cannot be used for surface mounting;
- resistance to high temperatures. When the current passes through it, the core heats up. It is necessary that the insulation can withstand both standard heating and short-term overloads;
- resistance to low temperatures. In the cold, some materials become very fragile and lose their basic properties;
- maximum allowable voltage. Almost all insulation materials can withstand voltages up to 1000 V, so when it comes to a private house, you can ignore this parameter.

Insulation can be made of the following materials:
- viscous resin impregnated paper, or rosin with oil, is one of the oldest insulation options. It withstands extreme operating conditions, high voltage, is inexpensive, but such a cable can not be laid in areas with a large slope. With a height difference of more than 25 m, a cable with non-draining impregnations is used. The insulation is afraid of moisture, so it must be enclosed in a protective sheath;

- rubber insulation It shows itself well in networks with direct current up to 10 kV and with alternating current up to 1 kV.Allows you to get the most flexible cable that is resistant to negative temperatures;

- PVC insulation (PVC) withstands low and high temperatures, up to +900C, resistant to moisture and aggressive substances. In the sun, the material gradually deteriorates, but thanks to special additives, it was possible to create insulation with increased resistance to frost, burning and the sun;

- XLPE insulation (SEE). In this insulation, the cables are lightweight and flexible. The coating is not afraid of moisture.

In addition to external insulation, a metal layer may be present. This is the so-called reservation, which allows you to make the cable as resistant to mechanical stress as possible. Armored cable is laid in moving soils and under highways.
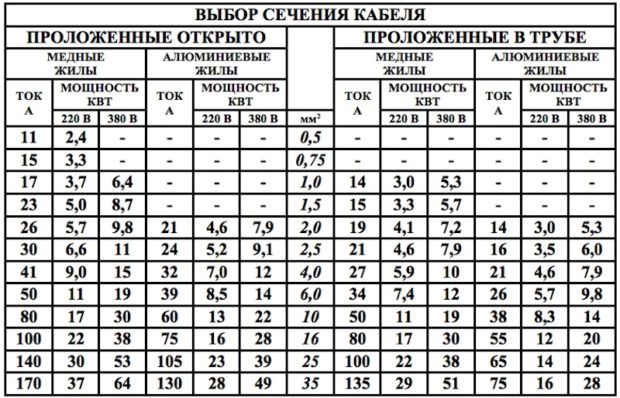
Number 4. Power cable section
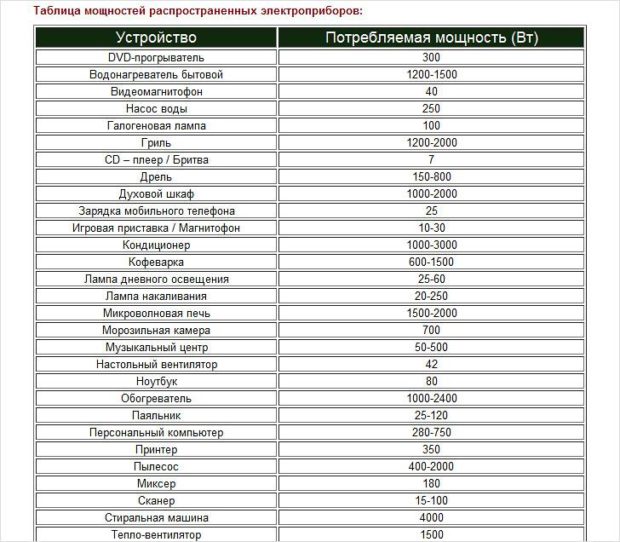
The choice of cable cross-section depends on what power all devices will consume and lighting technology in home. The higher the power, the thicker the cable must be in order to withstand the transmitted current without significant heating. When talking about the cross section of the power cable, they mean the cross section of the conductive wires, and not the diameter of the entire cable together with the protective sheaths.
Calculation of the required section can be performed according to the following simplified scheme:
- chart a future or existing wiring, mark all points of electricity consumption, determine their power;
- summarize the power of all appliances. Thus we get the maximum internal load;

- do not forget to take into account that new equipment may be bought in the future. Also, the old equipment can be replaced by a new and more powerful one;
- when the calculation of power consumption is made, it remains to divide this value by the voltage of the network (220 or 380 V), in order to finally obtain the current strength that the power cable will have to withstand;
- the electrical conductivity of the copper core is higher than that of aluminum, so with the same cross section it can conduct a current of higher strength. Special tables help to find the optimal cross-sectional value for copper and aluminum conductors with different installation methods.

Prefer grounding cable. If you plan to install an electric stove in the house, then it is better to take a cable with a cross section of more than 10 square meters. mm If you doubt the correctness of the calculations, it is better to consult with professionals who will tell you the optimal cross-section and the type of cable, based on the characteristics of electricity consumption.
Experts recommend checking the compliance of the declared section with the valid one. Often little-known manufacturers deceive the buyer, and all this is within the law. GOST provides for tolerance, and for some cables it reaches 15-30%.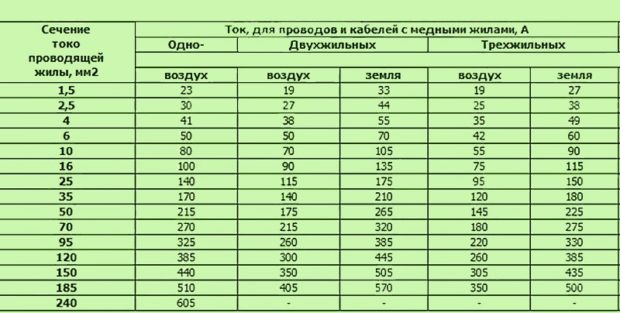
No. 5. Power Cable Labeling
Looking at the cable marking, an experienced person will immediately tell you what it was made of and in what conditions it is best used. According to Russian GOST, the letter marking:
- the first letter indicates which metal the current-carrying conductors are made of: for aluminum - A, for copper there is no designation;
- the second letter is the insulation material. If it is paper impregnated with resins - C (sometimes marking may be absent at all), if non-combustible rubber - HP, if PVC - B, if polyethylene - P, crosslinked polyethylene - Pv;
- the third letter - the features of the outer shell of the cores: A - aluminum, C - lead, P - polyethylene, B - polyvinyl chloride;
- the fourth letter indicates the type of armor, if any: K - galvanized wire round, P - galvanized wire flat, BBG - steel tape profiled, B - steel tape, Bn - steel tape with non-combustible coating;
- the fifth letter is the material of the outer cover, for example, a polyethylene hose (Шп), or a non-combustible composition (Н). In the absence of an outer cover in the marking put G;
- the sixth letter indicates various additional characteristics. For example, there is a cable that is off (ng).
The cable can be without armor, then there will be no corresponding symbol in the marking. The above are often found options for the execution of key elements, but in the marking you can see other letters, the meaning of which is presented in the table. Marking is applied to the cable in increments of 1 m.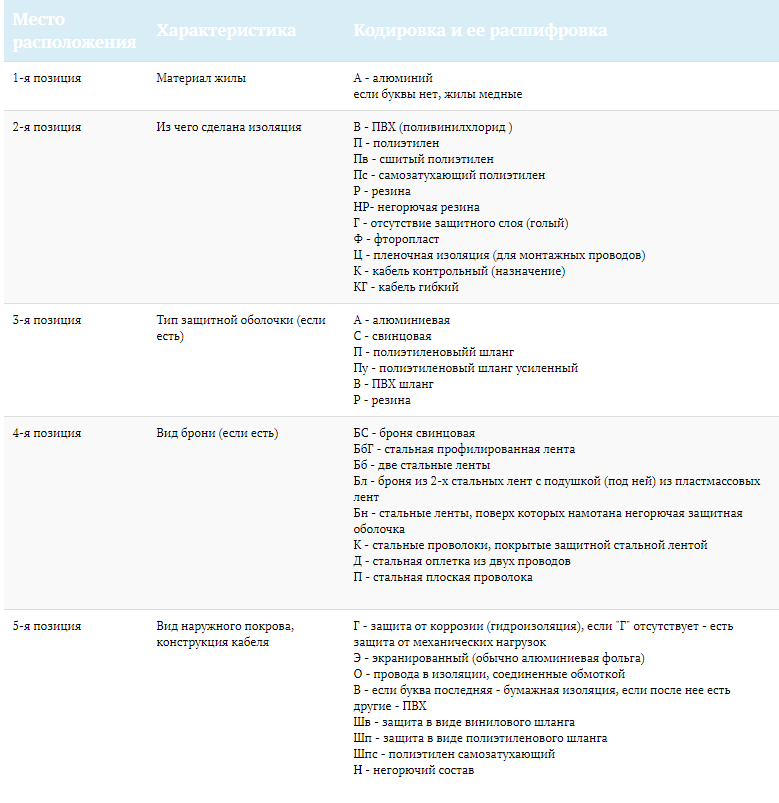
There are also digital notation, which indicate the number of cores and the cross-sectional area, as well as the presence of a zero core and its cross-section. For example, a cable with three conductors with a cross-section of 1.5 square meters. mm is marked as 3 * 1.5, and in the presence of a zero core you will see a plus sign, after which in the exact same form as for the current-carrying cable, the quantity and cross section for the zero core are indicated.
Foreign power cables are marked differently. So, for example, the letter Y stands for PVC insulation, C stands for copper screen, HX stands for XLPE, RG stands for armor.
Let's say we have a VVG power cable. This means that it is copper, since the first letter A.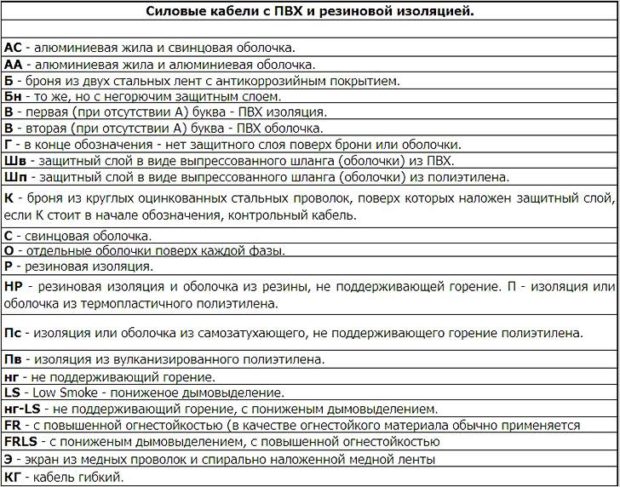
No. 6. Popular types of power cables
There are a lot of different modifications of power cables, but in private construction only some types of products are in special demand. We will consider them.
VVG
The cores can consist of one wire or several, in total from 1 to 5 cores in the cable, the cross section of the cores is 1.5-260 sq. mm It is sold in bays 100-200 m long, painted, as a rule, in black color, less often - in white.
VVG withstands from -50 to +500C, can work in high humidity, it is durable, resistant to aggressive chemicals. The cable is not very flexible. To rotate it at a right angle, it is necessary to provide a smooth bend equal to 10 section diameters.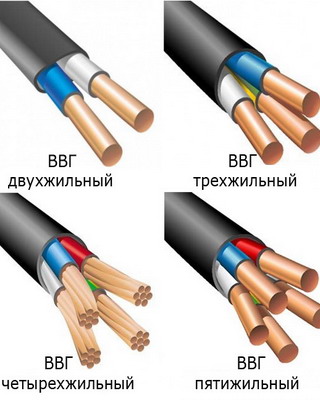
This popular type of cable has several modifications:
- VVGng - a cable in a protective casing, which provides maximum resistance to fire;
- AVVG - the same VVG, only with aluminum conductors;
- VVGp differs in a flat cable section, in some cases this option is more convenient in terms of installation;
- VVGz - cable with an additional layer of PVC or rubber between the insulation and the protective casing.
This type of cable is suitable for installation of networks up to 1000 V and a frequency of up to 50 Hz, often used for terrestrial and underground supply of electricity to the house.
NYM
This is a foreign analogue of the domestic VVG cable. For its production, only copper conductors are used, the profile is only round. Between the individual and general insulation there is a layer of coated rubber, due to which the cable receives additional fire resistance.
The cable consists of 2-5 cores, is designed for voltages up to 660 V, can withstand heat up to +700C and is even more flexible than the VVG cable: the bending radius of NYM is only 4 cable diameters.
NYM can be laid underground, but a corrugated pipe is best. The cable is afraid of sunshine.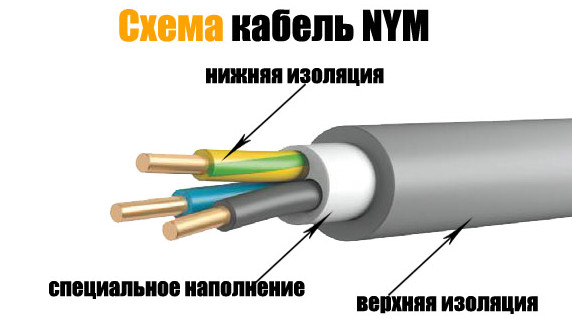
VBBSHV
Cable with 1-5 copper conductors with a cross section of 1.5-240 square meters. mm The internal and external insulation is made of PVC, the cavity between them is also filled with PVC. For reinforcement, two steel tapes are used that wrap the cable and hide under the outer sheath. The gaps between the turns of the first tape are hidden under the turns of the second tape. The cable is designed for a maximum of 1000 V, can be operated in a wide temperature range, like VVG. The bending radius is 10 diameters.
Modifications to this cable include:
- AVBBSHV with aluminum conductors;
- VBbShvng with non-combustible insulation;
- VBbShvng-LS - a cable whose insulation is not lit, and when smoldering emits a minimum of smoke.
The cable can be mounted underground in areas with increased explosion hazard, and it is also suitable for surface mounting when using sun protection.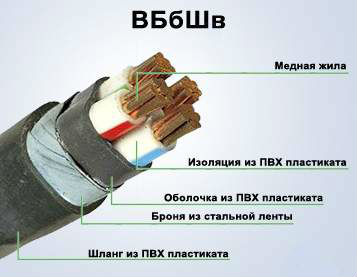
KG
Cable with general rubber insulation and rubber insulation of each core. The veins are copper, the flexibility is high, from 1 to 6 veins are inside. The maximum voltage is 660 V, the frequency is 400 Hz.The cable is expensive, so many prefer VVG. KG is well suited for connecting very powerful equipment, for example, welding machines, generators and other portable devices. Modification - KGng.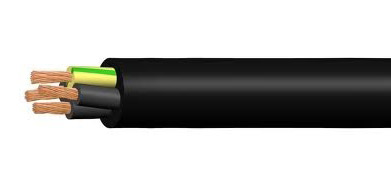
SIP
This is a separate category of power cables. SIP is a self-supporting insulated wire, the cores are made only of aluminum, there is no belt insulating layer. The possible cross-section of veins is from 16 to 150 square meters. mm The marking for this type of cable is specific. So, for example, SIP-1 is a cable with three cores, one of which is zero and simultaneously carrier.
The cable insulation is made of cross-linked polyethylene, so that it can withstand severe mechanical stress, exposure to sunlight and high humidity. SIP is great for electrifying private houses by land. Installation is necessary using special fittings.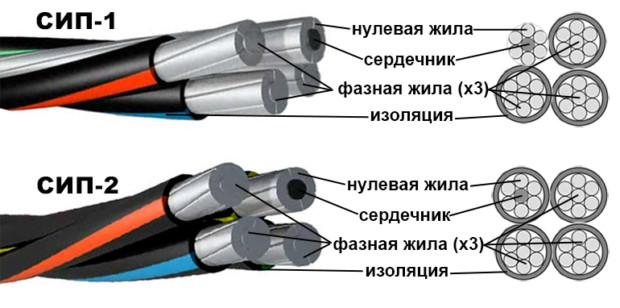
TsASBp
Aluminum conductors, one or more wires. The cable is distinguished by paper insulation and a lead alloy sheath, can withstand up to 10 kV. Use on inclined sections is allowed.
APvPu
Cable with aluminum conductors and cross-linked polyethylene sheath, suitable for installation in wet ground.
Number 7. Features of mounting a power cable
The cable can be laid:
- by air;
- underground.
The airborne installation method is easier to implement and cheaper. For this purpose, use the SIP, AVK cable, as well as AVVG and VVG with cable garter.
Under the ground, gusts of wind, rain and other weather factors do not act on the cable, but there is soil pressure and humidity. It is better to lay the cable away from the trees so that their roots do not damage the line. They use cable VBBSHV and AVBBSHV. Despite the durability of these products, it is better to use a plastic pipe to protect the cable from damage during subsidence.
If there is even a slight doubt about the correctness of one’s own choice, it’s better to once again ask a question to specialists than to redo everything later.